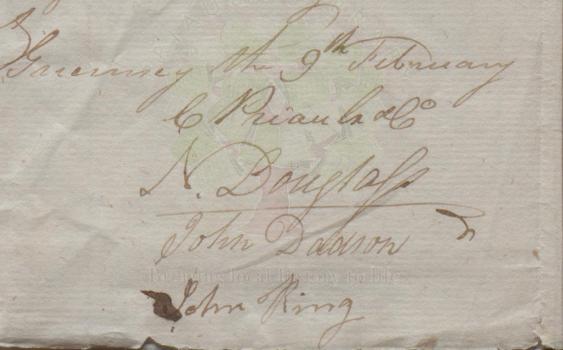9th July 2018
'A slightly coloured sketch.'An oaken chest, half eaten by the worm, But richly carved by Anthony of Trent, With Scripture stories from the life of Christ; A chest that came from Venice, and had held The ducal robes of some old ancestor. That by the way—it may be true or false.[From] Rogers’ Italy.By Samuel Elliott Hoskins. Victor Hugo was not, it would seem, the first to transform the carved wooden chests of Guernsey into some other form of decorative furniture. De Beauvoir De Lisle got there before him!
13th June 2017
By architect and wit Amias C Andros, published in the Star in 1879. See the two bound volumes of his press cuttings in the Library for further information. The illustration is A view from Marshall's Hotel, 1832, by Celia Markham (in the Priaulx Library collection.)
19th January 2017
Daniel Girard, Castle Porter, that is, prison warden/jailkeeper, lost his prisoner, George Pellew, who had been committed to his care by Jean Dobrée. Pellew owed Dobrée money. The Royal Court, under the auspices of the Juge-Délegué, William Le Marchant, had ruled on 8 March 1719 that Daniel Girard should not be required in any way to compensate Dobrée. Dobrée appealed to the Privy Council, who requested a report on precedents to the Royal Court. The following letter is what the Royal Court produced in reply; on reading it, the Privy Councillors confirmed the Royal Court's initial judgment and dismissed the appeal.
28th October 2016
From Old Guernsey Exhibition and Fair Souvenir Guide and Programme, St Martin's Parish Hall, Guernsey: T B Banks & Co., 1908, p. 29. The painting of the Queen Charlotte Inn above, a detail of a larger view of Cow Lane, dates from c. 1800; it exists only as a photograph, as its whereabouts since WWII are at present unknown. The colour image is a detail of a painting by Captain C Montague Jones, possibly based up on it, painted 50 years or so later. The original of the Jones watercolour is in the Guille-Allès Library, Guernsey.
29th September 2016
Will no. 175 from Edith Carey's set of transcripts, Wills & Legacies, Staff, in the Library.
13th September 2016
Tales of the shapeshifter Benez of the Clos du Valle. The woodcut is from Dr Thomas Bellamy's Pictorial Directory & Stranger's Guide to Guernsey, 1843, in the Library Collection.
8th September 2016
Guernsey Market Place [in 1809], with key. 1809 [1822]. 'Grand, grand old picture.' If you wish to reproduce any of these images, please contact a Librarian.
1st September 2016
Carteret Priaulx & Co set out the terms and conditions for agents for their privateer the New Daphné, in the Library's MS notebook 'List of privateers and prizes,' perhaps belonging originally to Ferdinand Brock Tupper. The same source lists the Daphne as a lugger captained by A Queripel in 1790, Patrick Harry in 1795, and then by John King. 'Agreed between Messrs C Priaulx & Co. & Messrs Ninian Douglas & John Dadson, the former on the one part acting for the owners of the New Daphné letter of Marque Capt John King bound from this port, to the Earl of St Vincent’s fleet & Gibraltar & the latter, for themselves going out, as Supercargo’s on the above letter of Marque on the voyage stipulated Viz:'
31st August 2016
An Act of the Privy Council concerning jurats, defining a quorum. In 1709, so many of the jurats had had to stand down in a case concerning prizes awarded to the Marlborough privateer that none had been left to judge the case. They had been stood down because they were related to either the plaintiffs or the defendants. This transcription comes from a MS notebook, Lists of privateers and prizes, in the Library collection.
22nd July 2016
Pierre Carey sends a specimen of an unusual tree from Guernsey to Sir Hans Sloane in London, in the hope of advancing medicine. His house, La Brasserie, or the Brewhouse (Carey was head of a very successful enterprise) was finally demolished in 1968. During Carey's lifetime La Brasserie had been home to one of the most splendid gardens in Guernsey.